What is the Best IP to Use: Choosing a Private DNS Range
Need to choose an IP address range for your home or office network? Don’t just grab any random range – there’s a lot more to consider.
What is an IP address?
The Simple Answer
An IP address is like a phone number for your computer or device. Just as a phone number helps people call you, an IP address helps other devices on the internet communicate with your device. It’s a unique set of numbers and letters that identify your device on a network.
The Technical Answer
An IP address is a unique number assigned to every device on a TCP/IP network. It acts as an identifier, allowing devices to connect to and communicate over the internet. There are two versions of IP addresses in common use: IPv4 and IPv6. IPv4 has four hexadecimal numbers separated by periods (e.g. 192.168.0.1), while IPv6 has six hexadecimal numbers separated by colons (e.g. 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334).

Through the use of DNS, which acts as an internet address book, humans can use domain names instead of numbers to navigate the internet and to address the devices on their network.
What is a private IP address range?
A private IP address range is a range of IP addresses that are reserved by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) for private use within a network.
They are set aside for use within private networks, such as a home,corporate or office network. These addresses are not publicly routable, meaning that they cannot be accessed over the internet. Instead, they are used to identify devices within the local network. The addresses we use online to access the internet are called ‘Public Addresses’.
The most commonly used private IP address ranges are:
- 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255 (10.0.0.0/8 prefix)
- 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255 (172.16.0.0/12 prefix)
- 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255 (192.168.0.0/16 prefix)
Using a private IP addresses allows for better network organization, security, and can also help conserve public IP addresses, as private IP addresses can be reused across different networks.
Network Host Address and Broadcast Address are also referred to in the context of private IP address ranges. These addresses are denoted by the number “255.255.255.255” and are used to denote a broadcast on a local hardware network.
With the introduction of Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) and its CIDR notation for expressing IP address ranges, it became easier to express IP address and its associated routing prefix. CIDR notation is constructed from an IP address, a slash (‘/’) character, and a decimal number which denotes the maximum size of the network.
What factors should you consider when choosing a private IP range for your network?
When choosing a private IP address range for your network, there are several factors to consider.
1. Compatibility
Make sure the IP range you choose is compatible with existing devices and services on your network.
It is also necessary to consider network Host Addresses and Broadcast Addresses. Generally, the “all ones” IP address (255.255.255.255) is used to denote a broadcast on a local hardware network, which must not be forwarded. “All zeros” is used to denote an unspecified address.
Subnetting
Consider how you plan to subnet your network, as this will affect the number of IP addresses available to you.
The location of a network can have a major impact on the choice of a private IP range.
Scalability:
Choose a private IP range that will be large enough to accommodate future growth in the number of devices on your network.
When it comes to private IP ranges, the amount of devices which can be connected before switching becomes necessary depends on the type of network being used. For example, with IPv4, there are 4.3 billion unique addresses available, allowing for many devices to be connected before it becomes necessary to switch.
Conversely, IPv6 raises the ceiling from 232 combinations to 2128, allowing for even more devices to be connected before switching becomes necessary. Additionally, IP address tracking tools can help to reconcile the configured devices with what your network has documented, ensuring accuracy and efficiency when it comes to IP address management.
Network topology
Consider your network topology and the number of layers, as this will affect the number of IP addresses needed.
When connecting clients that are located in multiple countries with different IP ranges, it is important to make sure that the IP ranges are not overlapping. For example, if you want to connect clients in the US, UK, and Canada, you could use the 10.x.x.x/8 range for the US, the 192.168 range for the UK, and the 172.16 range for Canada.
This ensures that the IP ranges do not overlap, preventing connection issues. It is also important to consider the number of devices that will be connected to the network, as well as the number of IP addresses that are needed. For larger networks with more devices, it is recommended to use a larger IP range such as the 10.x.x.x/8 range. Additionally, if the network requires extra security features or a kill switch, it is important to ensure that the IP range is configured to provide these features.
Security
Choose a private IP range that is not commonly used for public-facing networks, to minimize the risk of IP conflicts and cyber attacks.
Routing:
You should consider whether the private IP range you choose will be used for routing or not and if it will be used in connection with other networks.
Ultimately, the best IP range for a network depends on the size of the network, the security needs, the speed of the connection, and the type of service needed. By taking all of these factors into consideration, a network can be properly configured to suit the needs of the user.
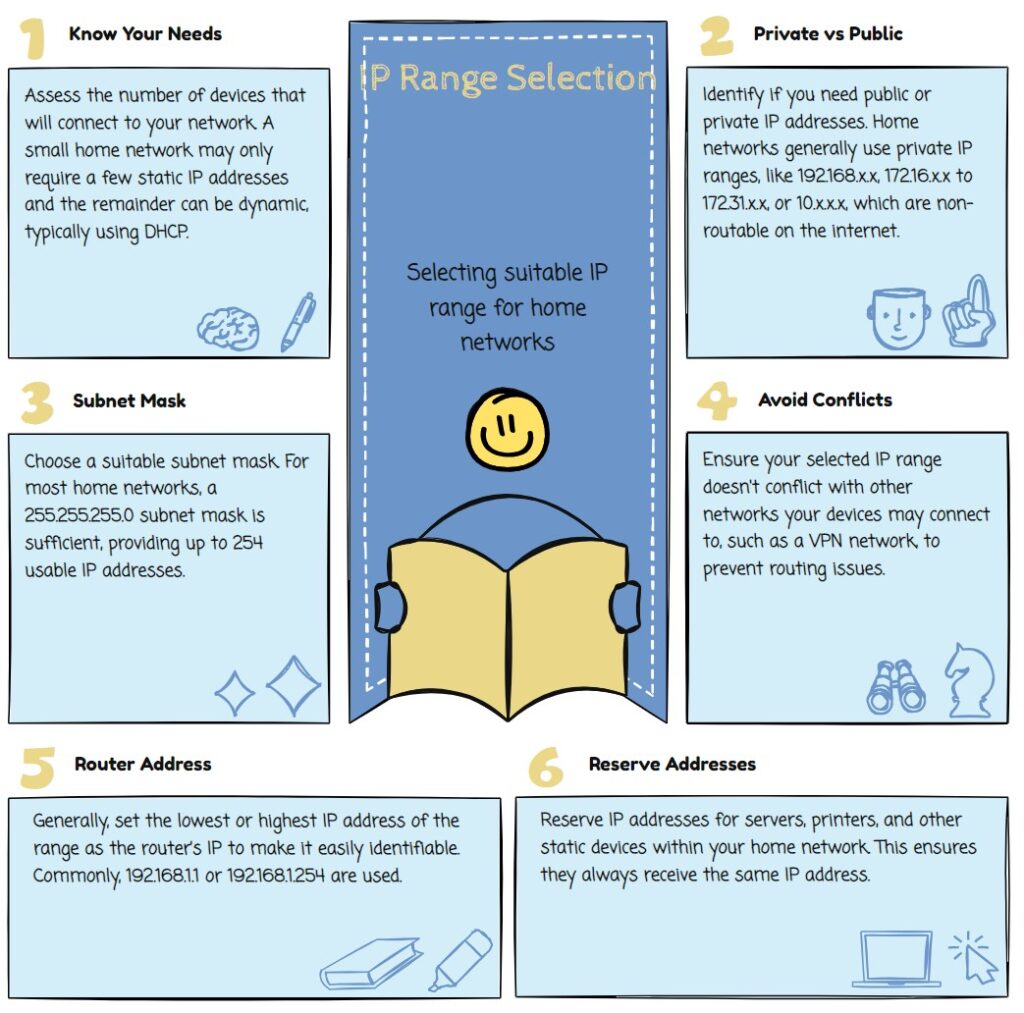
How to configure a device with a private IP address?
Step 1: Select the device type
The different device types for a private IP address include computers, laptops, smartphones, and tablets. To select one for a private IP address, you must first check the device that you are connected to in order to locate the IP address. Then, access the Properties of the network adapter that is currently connected to the device in order to configure the IP address. Once the IP address, subnet mask, and version of IP have been inputted, the OK buttons must be clicked in both windows in order for the settings to be saved. If you want to set your computer back to DHCP, you must select the “Obtain an IP address automatically” option in the Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) Properties window. You can access the network connections through ncpa.cpl in the Windows search bar.
Step 2: Select the private IP range
To select a private IP range for a device, you will need to follow these steps:
1. Go to the device’s settings and select “Network” or “Internet Settings”.
2. Select the option for “Use the following IP Address”.
3. Input the IP address, subnet mask and default gateway. For this tutorial, we will use IP address 192.168.10.10 and a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0. The default gateway should match the device’s IP address.
4. Save the settings and test the connection.
5. To ensure that the IP address is unique and doesn’t conflict with any other device on the network, you should select a high number for the last digit of the IP address between 100 and 254.
6. For more security, consider using a virtual private network (VPN), such as Avast SecureLine VPN.
Step 3: Configure the private IP address
Configuring a device with a private IP address can be done by following a few simple steps. First, you need to determine the IP address of the device that you are trying to connect to. Then, you need to set the IP address manually by going to Settings > Network > Set Up Internet Connection > Custom setup for LAN. For IP Address, switch to Manual and enter the IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, primary DNS, and secondary DNS. Finally, save your settings and test your internet connection to see if you can get back online. It is also possible to get a static IP address from your Internet Service Provider (ISP). If you do decide to get a static IP address, contact your ISP and request one. Then, you can enter the static IP address in the settings on your device.
Step 4: Set up automatic connection settings
To set up automatic connection settings for a device with a private IP address, follow these step-by-step instructions:
1. Go to the Settings menu and open the Network & Internet option.
2. Click on Properties under the local area connection field.
3. Click Edit under IP assignment.
4. Select Obtain an IP address automatically.
5. Click the OK button on the Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) Properties window and the OK button on the Ethernet Properties window.
6. Save the changes and test your internet connection to see if you can get back online.
Step 5: Make sure there is no public IP address available
To make sure there is no public IP address available when configuring a device with a private IP address, you can use the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) to automatically assign a random IP address on your network. To do this, go to the “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) Properties” window in the settings of your computer and click “Obtain an IP address automatically”. This will ensure that a random IP address is assigned to the device.
If you want to manually assign an IP address, you can select “Use the following IP Address” and input the IP address, subnet mask, default gateway and primary and secondary DNS of the device. To ensure that a public IP address is not used, make sure that the IP address is within the private range (e.g. 192.168.0.x). You can also contact your ISP and request a static IP address, which will also ensure that a public IP address is not used.
FAQs
What is an IP address?
An IP address is a unique number assigned to every device on a TCP/IP network. It is the digital equivalent of a physical address, which is used to identify computers and devices in order to allow them to communicate with each other. Internally, IP addresses are stored as numbers, while humans prefer names. The Domain Name System (DNS) is an internet address book that lets you use words (e.g. www.avast.com) instead of numbers to navigate the internet and address devices on your network. There are two versions of IP addresses in common use: IPv4 and IPv6. IPv4 has four hexadecimal numbers separated by periods (e.g. 192.168.0.1) while IPv6 has six hexadecimal numbers separated by colons (e.g. 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334).
What’s the Best IP Address for a home network?
The best IP address for a home network usually falls within the private IP address range. These ranges are:
– 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255
– 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255
– 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255
For a typical home network, a router will often assign local IP addresses, such as 192.168.1.x or 192.168.0.x, where x represents a variable number between 2 and 254. The specific IP address for a device may change based on other devices on the network, so the best IP address would be one that is not being used by another device.
How do I choose an ideal private IP range for my network?
Step 1: Understand the Problem
The issue is that many consumer hardware devices use the same IP range, 192.168.1.x, which is also used by the OpenVPN server setup in the home network. This makes it difficult to access devices on the home network over the VPN.
Step 2: Consider Possible Solutions
One option is to bring a spare router with you when travelling so that you can connect to your VPN without any issues. Another option is to change the IP range at home to one that is less likely to conflict.
Step 3: Research Available Options
The three standard blocks of RFC 1918 address ( 10.0.0.0/8 , 172.16.0.0/12 , and 192.168.0.0/16 ) are defined with wide netmasks, meaning that they can be subdivided however you like. Most people use a 24-bit block. Additionally, some users have recommended using 192.168.255.0/24.
Step 4: Choose the Best Option
Based on the research, the best option is to choose a network range within the 10.x.x.x or 172.x.x.x range that is not at the beginning of any of the big blocks. This will reduce the chances of conflicts. For example, some users have suggested using 192.168.50.0/24 or 172.16.0.0 go to 172.31.255.
What is the difference between static and dynamic IP addresses?
The primary difference between static and dynamic IP addresses is that static IP addresses remain the same while dynamic IP addresses are subject to change at times. Static IP addresses are typically used by businesses that host their own websites and internet services, while dynamic IP addresses are more common for home networks and consumer devices. static IP addresses are more expensive and may pose a greater security risk, while dynamic IP addresses are easier to manage and cheaper to deploy.
When using an ISP or cable provider, dynamic IP addresses are usually assigned automatically. Within one’s own network, devices can be manually assigned static IP addresses via the router’s interface. Generally, static IP addresses are better for businesses, while dynamic IP addresses are more suitable for home networks.
What is the difference between a router and a home router?
The main difference between a router and a home router is their purpose. A router is a networking device that is used to connect two or more networks together, allowing them to communicate with each other. It is typically used to connect a local area network (LAN) to an external network such as the Internet. Home routers are designed to provide a connection between a single home network and the outside world. They are used to provide security, forwarding of traffic, and other functions that are essential for running a home network.
In terms of functionality, routers are typically much more powerful than home routers. Routers typically come with more sophisticated features such as quality of service (QoS), firewall protection, and advanced routing capabilities. Home routers typically come with basic features such as port forwarding, wireless access, parental control, and basic firewall protection.
Routers also typically come with more ports and interfaces than home routers. Routers typically have multiple Ethernet ports, allowing them to connect to multiple networks simultaneously. Home routers typically only have a single Ethernet port, which is used to connect to a single home network.
Finally, routers and home routers come in different shapes and sizes. Routers are typically larger and more expensive than home routers, due to their increased functionality and complexity. Home routers are typically smaller, more affordable, and designed to be used in home networks.
What is a subnet and how is it used?
A subnet is a portion of an IP network that shares a common address component. Subnets are used to create logical groupings of networks and improve network performance, security, and scalability. When computers are connected to the internet, they must have a unique IP address that identifies them.
Each IP address consists of four sets of numbers separated by periods, and the first three sets of numbers designates the network and the fourth set of numbers designates the specific device.
A subnet mask is used to define the network portion of the IP address and the remaining bits are used to define the device. The subnet mask is usually expressed in the form of 255.255.255.0, which means that the first three sets of numbers (192.168.10.xx) represent the network, and the fourth set of numbers (xx) is used to identify the specific device. The subnet mask allows computers to communicate within the same network and helps to keep private information secure.
What is a NAT router?
NAT (Network Address Translation) routers are devices used to connect multiple computers and other devices to a single internet connection. It is a type of router that allows multiple devices to connect to the internet by translating the public IP address assigned to the router into many private IP addresses within the same network. This allows the router to provide each device with a unique IP address while still using the same public IP address. NAT routers also help to provide a layer of security by acting as a firewall between the local network and the public internet. By acting as a firewall, NAT routers can prevent malicious attacks and protect connected devices from unauthorized access.
What is a Default gateway?
A default gateway is an Internet Protocol (IP) address used by a computer to send data to another network or device. It is the router or other device that is responsible for forwarding packets to the appropriate destinations.
The default gateway is typically the router or modem used to connect the local network to the larger Internet. It is used to route traffic from the local network to the Internet and vice versa. By default, the default gateway is the IP address of the router or modem.
What is a DNS server and how does it work?
A DNS server is a system of servers that act as a directory for the internet. It translates domain names, like google.com or yahoo.com, into the IP addresses necessary for devices to load those internet resources. When you enter a URL into your browser, the DNS server communicates with other DNS servers around the world to find the right data response and connects you to the website you want.
The primary DNS servers are sometimes called the preferred DNS servers, while the secondary DNS servers are sometimes referred to as alternate DNS servers. Switching to different DNS servers may offer increased speed and privacy, as well as other benefits like content filtering and blocking of infected or phishing websites.
What is an IP address routing table and how is it used?
An IP address routing table is a data table used by a router to store the necessary information in order to route IP packets as they travel across a network. It contains entries that map a destination IP address to a specific router that knows how to reach that particular address.
This data table is used by the router to identify the best route for a given IP packet to take in order to reach its destination. The router will use this table to forward the packet to the next router until it finally reaches its destination. The routing table can also contain entries that indicate a default route, which is a route used when no specific route is available.
What’s the Best IP Address to use?
Any IP address that works is arguably the best address to use. However because of geo-location ideally your IP address should be registered in the same country as the resources you visit most often.

Thanks for this, was trying to pick an IP address range for my home lab -very useful information.